Neutrophil modulation during cerebral ischemia by the nuclear receptor NR4A1
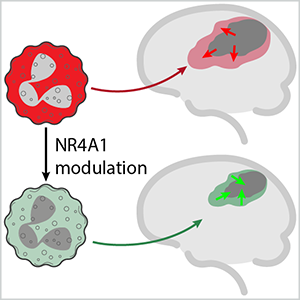
Sterile inflammation upon cerebral ischemia is accompanied by immune cell infiltration. Neutrophils exert a crucial role within the inflammatory response and finally on neuronal damage via interaction with other immune cells of the innate and adaptive immune system. However, unselective blockade of brain neutrophil infiltration has so far been unsuccessful in clinical studies. We hypothesize that neutrophils are differentially modulated in the context of stroke, that the nuclear receptor NR4A1 is critically involved and that pharmacological modulation of NR4A1 opens the possibility of a fine-tuned therapeutic intervention.
Team
Publications
CD177 Expression on Neutrophils Predicts Ischemic Stroke Outcome in HumansGronewold, J.; Hagemann, N.; Zhang, Y.; Jung, M.; Fleischer, M.; Mohamud Yusuf, A.; Li, A.; Wang, C.; Dzyubenko, E.; Scholtysik, R.; Klein-Hitpass, L.; Kraus, A.; Tuz, A. A.; Singh, V.; Frank, B.; Mönig, A.; Giese, A.; Graser, C.; Niklas, E. M.; Da Silva Rafael, M.; Nanthagopal, M.; Neumann, J.; Kufner, A.; Liman, T. G.; Liu, Y.; Minnerup, J.; Klotz, L.; Giebel, B.; Tertel, T.; Endres, M.; Hermann, D. M.; Gunzer, M.
2026 Stroke
|
The Nuclear Receptor NR4A1 Serves as a Neutrophil-Intrinsic Regulator Mitigating Stroke SeverityStrecker, J.-K.; Schmidt, Y.; Liebmann, M.; Walter, C.; Roth, S.; Aleth, H.; Börsch, A.-L.; Schmidt-Pogoda, A.; Beuker, C.; Yusuf, A. M.; Revenstorff, J.; Osei-Sarpong, C.; Krafft, L.; Schwarze, A.-S.; Heming, M.; Richter, M.; Kuhlmann, T.; Hucke, S.; Heming, J.-N.; Hansen, U.; Hagemann, N.; Bader, A.; Gao, J.; Walzog, B.; Maier-Begandt, D.; Chevre, R.; Hanschmann, E.-M.; Lücke, M.; Sommer, C.; Hermann, D. M.; Roth, J.; Thomas, C.; Meyer Zu Hörste, G.; Gunzer, M.; Vogl, T.; Zarbock, A.; Rosenbauer, F.; Silvestre-Roig, C.; Söhnlein, O.; Klotz, L.; Minnerup, J.
2025 bioRxiv
|
Neutrophil Progenitor Mobilization Is a Distinct Feature of STEMI and Predicts SurvivalRichter, M.; Von Göwels*, J.; Fähndrich*, M.; Fernandez*, C. L.; Grohn*, K.; Schwarz, D.; Lang, A.; Polzin, A.; Farinola, L.; Gosh, S.; Groba, S. R.; Heming, J.-N.; Aleth, H.; Rübsamen, N.; Radecke, T.; Rosenbauer, F.; Sickmann, A.; Karch, A.; Zarbock, A.; Minnerup, J.; Sindermann, J.; Bender, A.; Rossaint, J.; Ormanns, S.; Gunzer, M.; Reinecke, H.; Makowski, L.; Jung, C.; Silvestre-Roig, C.; Kelm, M.; Gerdes, N.; Chevre, R.; Lange, S.; Soehnlein, O.
2025 Research Square
|
Broad Rim Lesions Are a New Pathological and Imaging Biomarker for Rapid Disease Progression in Multiple SclerosisKlotz, L.; Smolders, J.; Lehto, J.; Matilainen, M.; Lütje, L.; Buchholz, L.; Albrecht, S.; Walter, C.; Varghese, J.; Wiendl, H.; Nylund, M.; Thomas, C.; Gardberg, M.; van den Bosch, A. M. R.; Airas, L.; Huitinga, I.; Kuhlmann, T.
2025 Nat Med
|
Endurance Exercise Attenuates Established Progressive Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis and Is Associated with an Amelioration of Innate Immune Responses in NOD MiceSchiffmann, D.; Lampkemeyer, V.; Lindner, M.; Fleck, A.-K.; Koch, K.; Eschborn, M.; Liebmann, M.; Strecker, J.-K.; Minnerup, J.; Wiendl, H.; Klotz, L.
2023 Int J Mol Sci
|
Neutrophils - Biology and DiversityMaier-Begandt, D.; Alonso-Gonzalez, N.; Klotz, L.; Erpenbeck, L.; Jablonska, J.; Immler, R.; Hasenberg, A.; Mueller, T. T.; Herrero-Cervera, A.; Aranda-Pardos, I.; Flora, K.; Zarbock, A.; Brandau, S.; Schulz, C.; Soehnlein, O.; Steiger, S.; the TRR332 consortium.
2023 Nephrol Dial Transplant
|
Alarming and Calming: Opposing Roles of S100A8/S100A9 Dimers and Tetramers on MonocytesRusso, A.; Schürmann, H.; Brandt, M.; Scholz, K.; Matos, A. L. L.; Grill, D.; Revenstorff, J.; Rembrink, M.; von Wulffen, M.; Fischer-Riepe, L.; Hanley, P. J.; Häcker, H.; Prünster, M.; Sánchez-Madrid, F.; Hermann, S.; Klotz, L.; Gerke, V.; Betz, T.; Vogl, T.; Roth, J.
2022 Advanced Science
|
Neutrophils in aging and aging-related pathologiesVan Avondt, K.; Strecker, J.-K.; Tulotta, C.; Minnerup, J.; Schulz, C.; Soehnlein, O.
2022 Immunol Rev
|