Metabolic control of neutrophil swarming and cluster formation
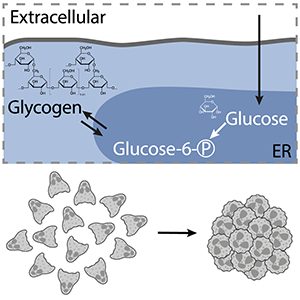
Neutrophil swarming and cluster formation are critical processes of the neutrophil tissue response. Intercellular communication allows many individual neutrophils to coordinate their dynamics and concentrate their combined effector functions at local sites of tissue injury, inflammation or infection. Swarming responses are essential for containing lesioned tissue sites during sterile inflammation and infections. Neutrophil swarming results from a coordinated sequence of individual cell responses, including cell activation, phagocytosis, migration, secretion of lipid mediators and the release of anti-microbial compounds, each of which could be differentially controlled by specific metabolic pathways. We here aim at investigating critical metabolic pathways, in particular glucose metabolism, that underlie the self-organization behavior of swarming neutrophils.
Team
Publications
The Arp2/3 Complex Controls the Development of Homeostatic MicrogliaSafaiyan, S.; Frosch, M.; Bickel, T.; Monaco, G.; Dvir, R.; Madry, C.; Bosch, L. F. P.; Kierdorf, K.; Innocenti, M.; Priller, J.; Prinz, M.; Lämmermann, T.
2026 EMBO Rep
|
TSP1/TGF-Β1 Drives Arachidonic Acid Metabolism to Orchestrate Neutrophil SwarmingWidera, L.; Spangenberg, P.; Siemes, D.; Bessler, S.; Bottek, J.; Voss, H.; Novak, A.; Hueser, D.; Richter, M.; Potthoff, A.; Siebels, B.; Moritz, M.; Gocke, A.; Thiebes, S.; Tautges, S.; Chavakis, T.; Jablonska, J.; Lämmermann, T.; Gunzer, M.; Schlüter, H.; Hahn, J.; Grüneboom, A.; Soehnlein, O.; Dreisewerd, K.; Soltwisch, J.; Shevchuk, O.; Engel, D. R.
2025 bioRxiv
|
Early Microglia Progenitors Colonize the Embryonic CNS via Integrin-Mediated Migration from the Pial SurfacePetry, P.; Oschwald, A.; Merkt, S.; Dinh, T.-L. J.; Andrieux, G.; Crisand, C.; Botterer, H.; Nent, E.; Paterson, N.; Havermans, M.; Sankowski, R.; Schilling, O.; Boerries, M.; Amann, L.; Groß, O.; Schlitzer, A.; Prinz, M.; Lämmermann, T.; Kierdorf, K.
2025 Dev Cell
|
Extrasinusoidal Macrophages Are a Distinct Subset of Immunologically Active Dural MacrophagesAmann, L.; Fell, A.; Monaco, G.; Sankowski, R.; Wu, H. Z. Q.; Jordão, M. J. C.; Borst, K.; Fliegauf, M.; Masuda, T.; Ardura-Fabregat, A.; Paterson, N.; Nent, E.; Cook, J.; Staszewski, O.; Mossad, O.; Falk, T.; Louveau, A.; Smirnov, I.; Kipnis, J.; Lämmermann, T.; Prinz, M.
2024 Sci Immunol
|
Extrasinusoidal Macrophages Are a Distinct Subset of Immunologically Active Dural MacrophagesAmann, L.; Fell, A.; Monaco, G.; Sankowski, R.; Wu, H. Z. Q.; Jordão, M. J. C.; Borst, K.; Fliegauf, M.; Masuda, T.; Ardura-Fabregat, A.; Paterson, N.; Nent, E.; Cook, J.; Staszewski, O.; Mossad, O.; Falk, T.; Louveau, A.; Smirnov, I.; Kipnis, J.; Lämmermann, T.; Prinz, M.
2024 Sci Immunol
|
Neutrophil trapping and nexocytosis, mast cell-mediated processes for inflammatory signal relayMihlan, M.; Wissmann, S.; Gavrilov, A.; Kaltenbach, L.; Britz, M.; Franke, K.; Hummel, B.; Imle, A.; Suzuki, R.; Stecher, M.; Glaser, K. M.; Lorentz, A.; Carmeliet, P.; Yokomizo, T.; Hilgendorf, I.; Sawarkar, R.; Diz-Muñoz, A.; Buescher, J. M.; Mittler, G.; Maurer, M.; Krause, K.; Babina, M.; Erpenbeck, L.; Frank, M.; Rambold, A. S.; Lämmermann, T.
2024 Cell
|